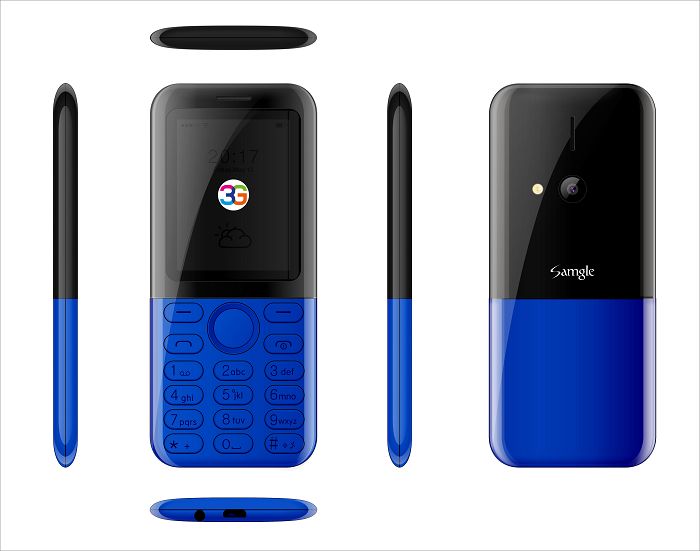

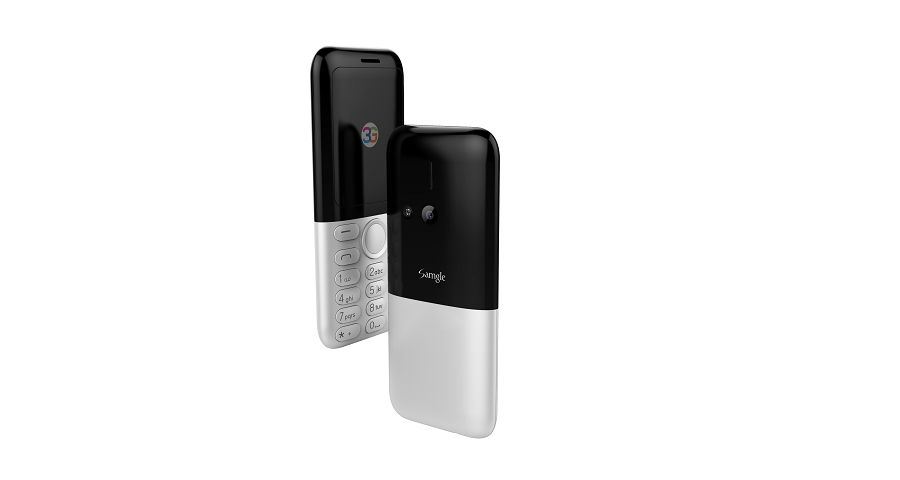
3310X 3G Low Cost Senior Phone
-
Min Order
1
-
Product Unit
Pieces
-
Origin
China Mainland
-
Payment


- Contact Now Start Order
- Favorites Share
- Description
Product Detail
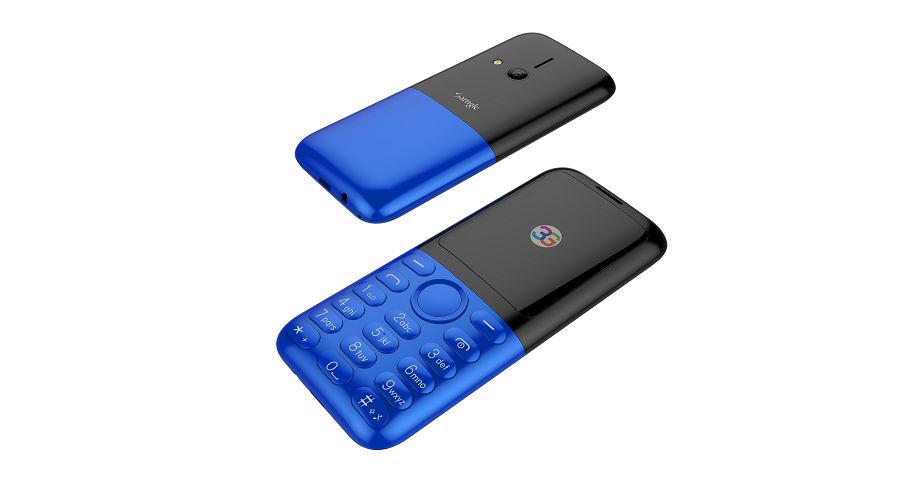
We believe firmly that the 3D screen and color match used by both Samgle 3310 X 3G will impress you profoundly.
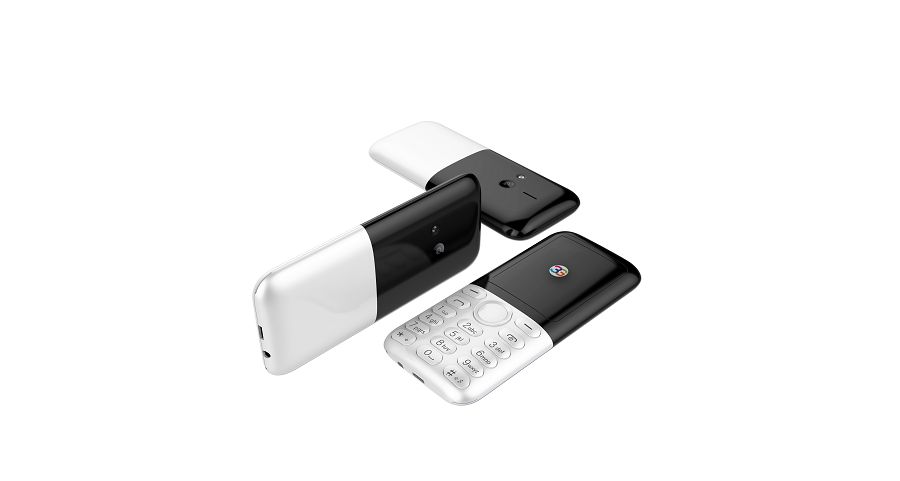
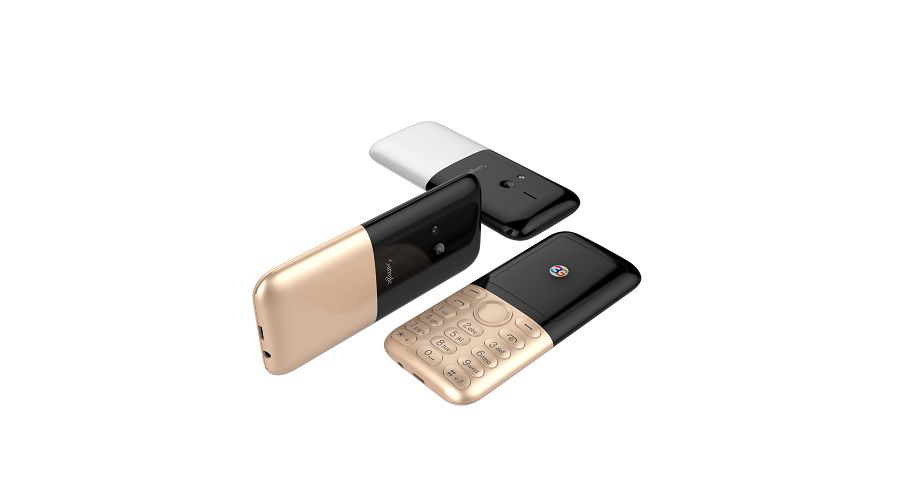
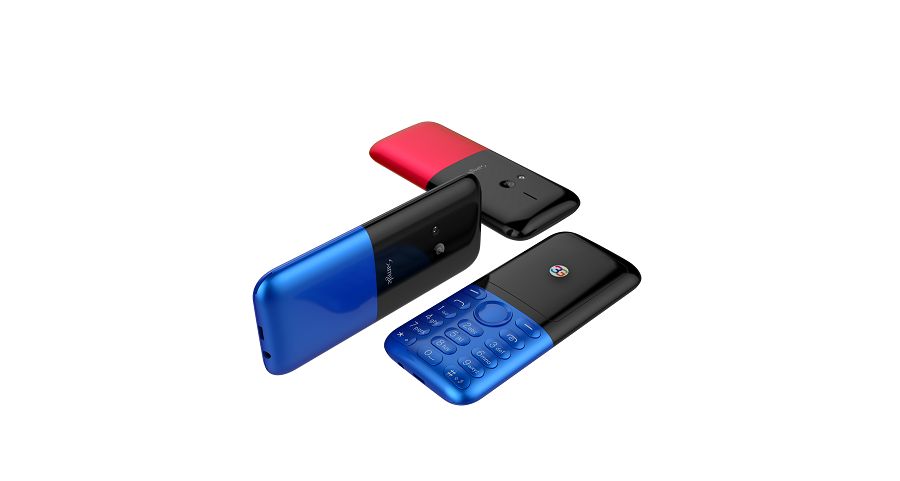
Samgle 3G 3310 X comes in 4 color variants, Black, Red, Blue, Gold
Tip:
Unlocked for Worldwide use. Please ensure local area network is compatible. click here for Network Frequency of your country. Please check with your carrier/provider before purchasing this item.
Samgle 3310 X 3G Unlocked Phone Bluetooth Dual SIM 0.08MP Camera 3D Screen
Main Features:
Back Camera: 0.08MP ( SW 2.0MP )
Display: 2.4 inch screen
Dual SIM Dual Standby: dual standard SIM
RAM + ROM: 64MB RAM + 128MB ROM
Battery: 850mAh li-ion battery
Bluetooth: V2.1 + EDR
Networks:
2G: GSM 850/900/1800/1900MHz
3G: WCDMA 900/2100MHz
Specification
Basic Information | Brand: Samgle |
Network | Network type: GSM+WCDMA |
Display | Screen type: Capacitive |
Camera | Camera type: Single camera |
Connectivity | SIM Card Slot: Dual SIM, Dual Standby |
Media Formats | Music format: AMR, MP2, MP3, WAV |
Languages | Languages: English, Espanol, Portuguese, Italian, German, French, Russian, Arabic, Poland, Dutch, Bahasa Melayu, Chinese, Hindi, Tamil, Thai, Myanmar |
Additional Features | Additional Features: Alarm, Bluetooth, Calculator, Calendar, FM, MP3, MP4, Sound Recorder, Wi-Fi |
Package Contents | Cell Phone: 1 |
Dimensions | Product size: 12.70 x 5.50 x 1.50 cm / 5 x 2.17 x 0.59 inches |
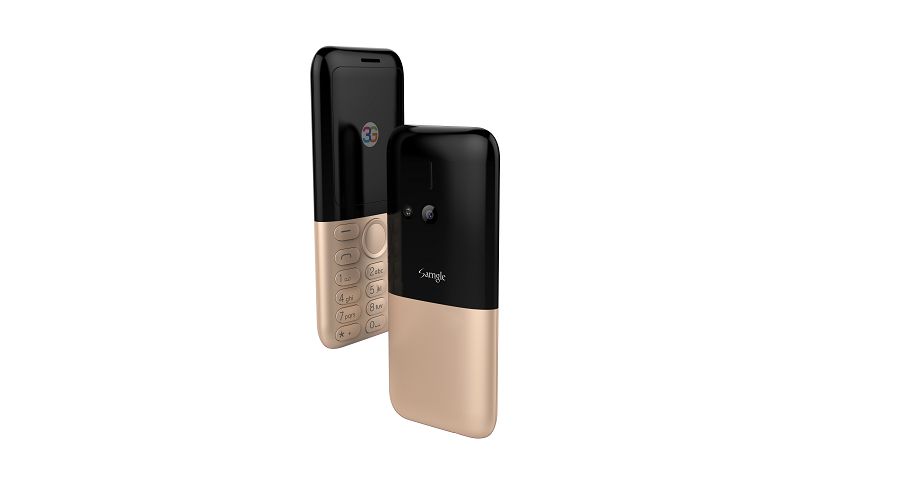
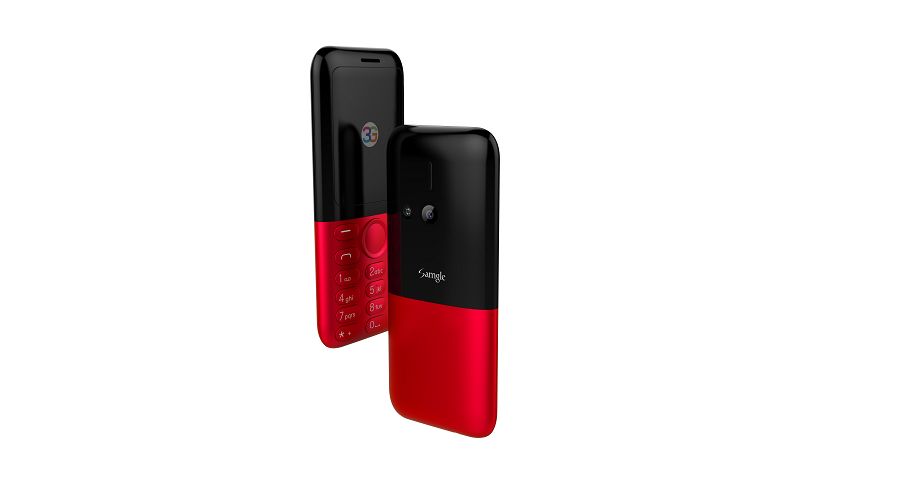
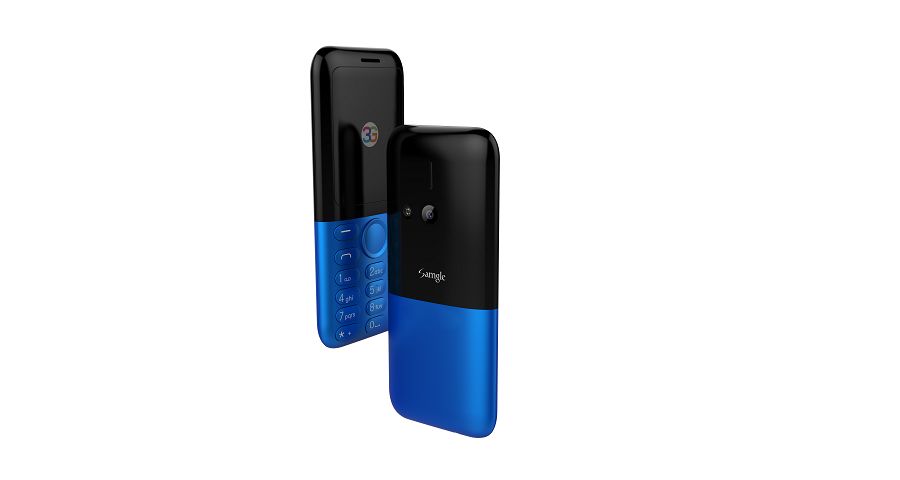
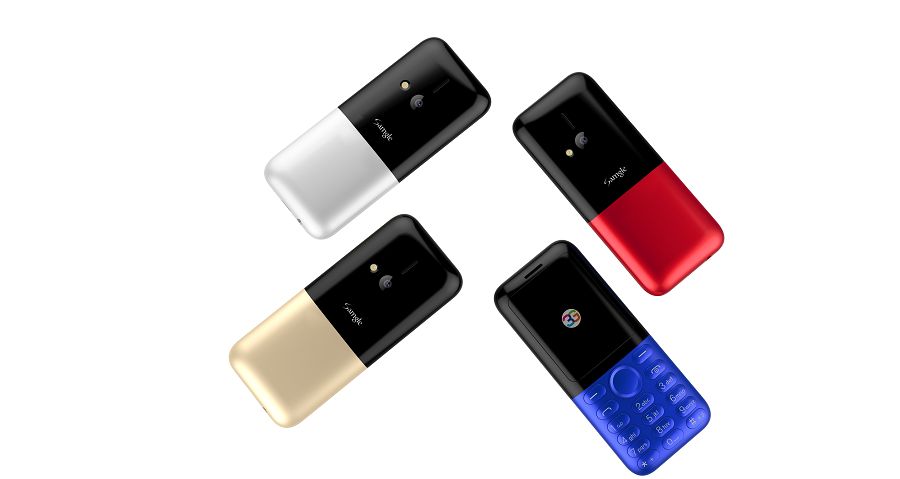
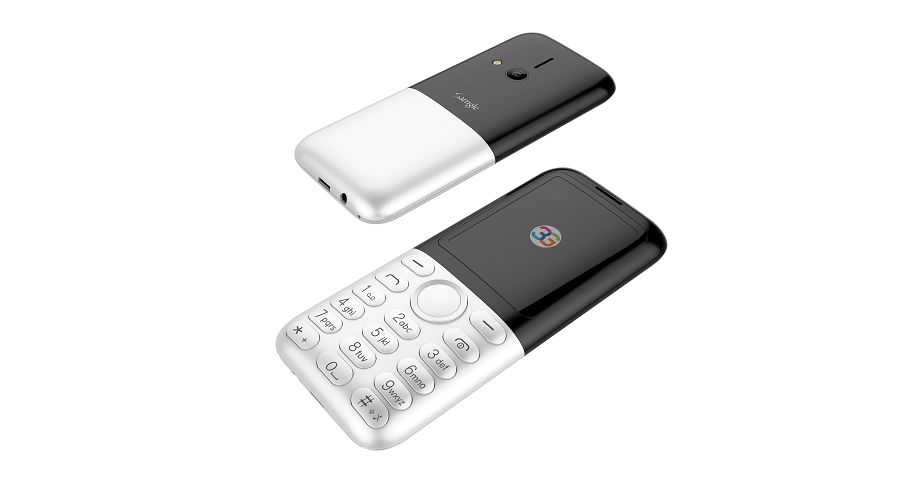
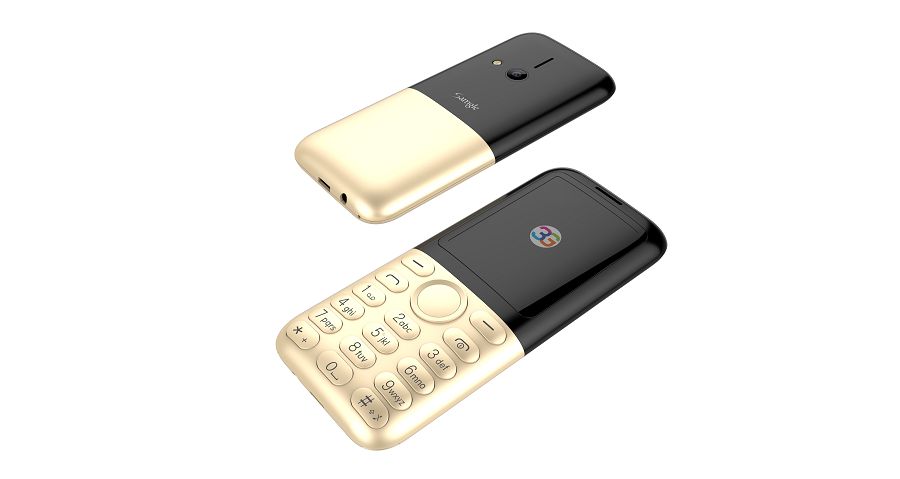
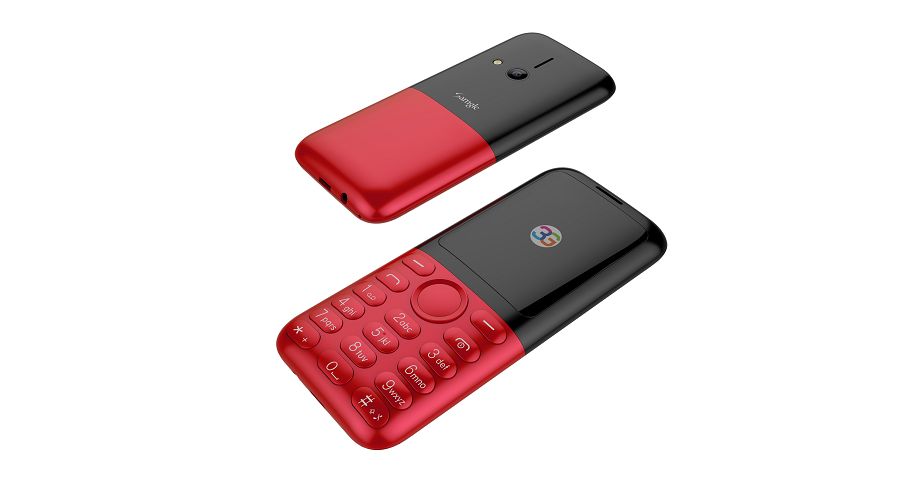

















Q: It does work in Malta, EU? Can this mobile be Branded ? If it works in Malta I want to put my Logo on them and order a big quantity.
A: This phone will only work with GSM networks: GSM 850 /900 /1800 / 1900MHz, 3G:WCDMA 900/2100
Please check with your carrier / provider before purchasing this item.
Please note that it can be Branded
Q: Is this model really installed in Czech?Language Russian?
A: Thanks for your inquiry.
English, Espanol, Portuguese, Italian, German, French, Russian, Arabic, Poland, Dutch, Bahasa Melayu, Chinese, Hindi, Tamil, Thai, myanmar,
Please note that it can be set to Russian
Q: What's the operating system, is it Android? Which version?
A: This item comes without operating system.
Q: hello, does this phone have the feature to record incoming calls?thank you
A: Thanks for your inquiry.
Please note that it has the call records
Q: Does this phone have GPS, Thank you
A: Sorry that this phone doesn't have GPS,
Q: Does this phone work in Portugal and is it available in Portuguese?
A: Please check with your local communication company if they suport this network frequency:
GSM: 850/900/1800/1900MHz
WCDMA:900/2100,
Yes, it has Portuguese language
Q: Hi there I was wondering if this phone works in Australia 3G or 4g or 5 g networks thank you
A: This phone will work with GSM networks: 2g:GSM 850/900/1800/1900MHz .
3G: WCDMA 900/2100MHz
Q: Will this phone support network service providers in Canada?
A: It just can work with Networks:
2G GSM: GSM 850/900/1800/1900MHz.
3G WCDMA: 900/2100
What is the Difference Between HSPA+ and HSPA?
High Speed Packet Access (HSPA) technology, the most widely used mobile broadband technology, has made it possible to download more data faster on third generation (3G) mobile broadband networks. The mobile telephony protocol improves the speed and capacity of current wideband code division multiple access (WCDMA) wireless broadband networks by more efficiently using the broadband spectrum. Evolved HSPA (HSPA+) uses the spectrum more efficiently, allowing for higher peak data rates and fewer delays in data transmission. These key differences between HSPA and HSPA+ generally make the second a more efficient choice for 3G networks.
The main advance in HSPA over older technologies is improvement in the protocols, or communications rules, that facilitate the movement of voice and data packets between hand-held devices and base stations. Communications network engineers work to improve the speed, amount of data per channel, number of channels, error detection, and methods of data encoding and decoding. As a result of these more efficient protocols, users of broadband-hungry multimedia services can download content quicker. Users, for example, are less likely to experience the delayed buffering of video that was indicative of older generation air interface protocols.
HSPA is the combination of high speed downlink packet access (HSDPA) and high-speed uplink packet access (HSUPA) protocols. It downloads at a peak data rate of 14 megabits per second (Mbps) and uploads at 5.8 Mbps. Specifically, it optimizes the use of the WCDMA radio bandwidth by increasing the transmission rate, sharing channel transmission, shortening the time between transmission intervals, and improving the modulation and amplitude of the signal.
The plus in HSPA+ signifies an even faster and more efficient use of the spectrum. This technology provides peak download rates of up to 56 Mbps and peak uploads of 22 Mbps. The most significant advance in HSPA+ is that it can operate on an all-Internet protocol (IP) architecture — the evolutionary goal of mobile telephony. An IP architecture makes more direct connections within the broadband network, helping to lower the cost of moving a megabyte of data and reduce latency — the delays in information processing typically unnoticeable to humans. The result is an always-on connection and improved response times.
HSPA and HSPA+ technology are based on the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), used by 80% of carriers worldwide. Network providers are upgrading to this technology, and continuing to improve the speed and capacity of high-speed data transmissions. Handset makers are keeping pace by introducing a broad range of compatible cell phones and smart phones.
What is an Electrostatic Motor?
An electrostatic motor uses the attraction and repulsion of an electric charge to generate energy. This is also known as a capacitor motor and is a type of eclectic motor. The electrostatic motor is most commonly used in micro-mechanical systems to create a drive voltage of less than 100 volts.
The first electrostatic motors were developed by Benjamin Franklin and Andrew Gordon in the mid-1700s. The motor originally was used to power bells and other small devices. The motor is based on the use of moving plates that are charged to be either positive or negative. The forces that generate the power do not wear down the plates, resulting in a long-term, stable method of energy generation.
An electrostatic motor can be created from standard household items and is a great science fair project. The amount of energy generated is not very large, but it is steady, does not require any consumable materials and has no residual products. The level of output usually is less than 100 volts, and the motor can be quickly disassembled, if required.
The energy in an electrostatic motor is created through static electricity. To create the motor, simply charge two items: one positive and one negative. Make a simple fan by attaching blades to an upside-down cup and attaching the base of the cup to a stick to allow free movement. Move the positive and negative items close together over the fan and watch it move. This is an electrostatic motor in action.
The invention of dry cell batteries and flowing electricity quickly replaced the electrostatic motor as an option for consumers. The development of computer circuitry, however, has revitalized the use of this type of motor. These electronic boards are very sensitive to spikes in power. The electrostatic motor creates a steady, low level of energy that presents no risk to the circuitry.
People who work in electronics or electrical engineering typically are very familiar with the electrostatic motor, and they often have built this motor as a science project and can see how the concepts can be applied to other projects or challenges. For example, electrostatic painting uses a very similar concept, because the surface is negatively charged, and the paint positively charged. As the item moves through the paining machine, the paint is released and is naturally attracted to the surface. This creates a smooth, even application with minimal effort. At the end of the process, the charge is neutralized, allowing the material to pass to the next stage with no interruptions.
How can I Unlock Cell Phones?
Cell phone service providers routinely program the cell phones they offer to their customers so that these phones cannot be used with another carrier. Phones that are carrier-specific are referred to as being locked. This tactic often keeps users from switching from one provider to another, but can be frustrating if you have good reason to change, but don’t want to lose your current phone.
People who travel to Asia or Europe are often faced with a dilemma when it comes to using their cell phones. U.S. cell phone carriers charge international travelers high roaming fees, often making using a cell phone overseas cost-prohibitive. The solution is to purchase a SIM card from the cell phone company in the country in which you are traveling. Many international companies sell cards pre-loaded with minutes and if your phone is unlocked, you can switch out the SIM cards and use your phone.
The ability to unlock cell phones depends on the type of phone you have and the technology associated with it. Currently, cell phones are equipped with either Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) or Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM). CDMA technology utilizes the entire available spectrum, enabling users far greater capacity that GSM, which assigns each user a subscriber identity module (SIM) card. This card holds all the user’s phone settings, contacts, notifications, and call history.
While a CDMA phone offer better coverage, because it must be programmed by the carrier and does not have a removable memory card, it cannot be unlocked. With a GSM phone, however, it is often possible to switch the SIM card from one phone to another, allowing service to continue uninterrupted.
This is not always possible, however. Some phones are programmed with software that links the SIM card to the serial number of a specific phone. The serial number of the phone must match the code on the SIM card in order for the phone to work. This restricts switching the SIM card to another phone or the specific phone to another SIM card.
There are four ways to unlock cell phones. Start by calling your service provider and asking them the procedure for unlocking a phone. Depending on the company’s policy, they may charge a fee to do this. You may also have to agree to remain with the company for a specific amount of time. If the terms are acceptable, the process is simple. The CSR will give you a code, which you can enter into your phone and it will be unlocked. Another method is to use a company that offers a fee to unlock cell phones. To find one of these companies, search for "unlock cell phones" using your favorite Internet search engine.
You can also unlock cell phones by using special equipment such as a universal unlock SIM card, a data card unlocker, and a data cable with standalone software. This equipment can be pricey, however, and is most often used by professionals operating cell phone unlock services.
The final way to unlock cell phones is by using the online community. There are numerous phone unlocking forums and message boards where people share information, including unlock codes, company policies, and other pertinent information.
Once your phone is unlocked, you can install a new SIM card and switch providers. You may want to check the terms of the original provider’s contract, however, in that many cell phone companies charge hefty fees to drop service.
What is a GPRS System?
General packet radio service (GPRS) is a data transfer specification used by Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), and Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), networks. The GPRS system makes use of the entire coverage area and frequency of its host networks to transmit data packets. Data packets are segments of data sent between computers or network devices. These mobile technologies work together to handle most of the world's mobile communications.
The GPRS system sits on top of the TDMA and GSM networks to provide subscribers uninterrupted data connection instead of a dial-up connection. This gives subscribers the ability to access data without the need to dial up and authenticate. A packet control unit is present in a GPRS cellphone. This control unit provides a bridge for data to travel across mobile networks and the Internet by making use of radio channels.
Eliminating the need to use voice channels to transmit data, GPRS gives network providers a more efficient way to deliver data to their users. Using a GPRS connection ensures subscribers four times the speed of most traditional dial-up connections. Dial-up data services offer an average speed of 9.6 kbps while GPRS offers a speed of 40 to 172.2 kbps. GPRS communication also gives subscribers the ability to stream rich media applications and content. There is no need to download the content before it can be viewed or used. This makes the GPRS system ideal for web browsing from mobile devices.
Rich media applications are made available through mobile connection because of the GPRS system. These applications were previously unavailable in GSM networks due to the speed limitations of circuit switched data and the message length of short message service (SMS) which is 160 characters. The GPRS system allows applications that were previously exclusive to desktop computers and laptops to be used in mobile networks. It opens up a whole lot of possibilities in terms of new technology and fresh ideas.
A GPRS network also enables mobile Internet functionality. This means that the services available on the Internet such as web browsing, email, chat and file transfer protocol (FTP) can be accessed through mobile devices. Using the same protocols, the GPRS network can be considered as a sub-network of the Internet while the GPRS cellphones can be viewed as mobile hosts. Technically, every GPRS device can be assigned its own Internet Protocol (IP) address. GPRS works on cellphones, laptops and other portable devices with a GPRS modem or a GPRS Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card. In using a computer to send and receive messages, a GPRS modem is recommended.
- Mobile Bridge 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Crane 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Bridge 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Bridge C 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Bridge 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Lifts 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Magic Box Mobile Powerbank 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- 12000 Giant Mobile Power 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Cel Phones 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- HSP Mobile NET Device 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Speaker 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Cleaner 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Toolbox 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Cranes 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Billboard 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Lift 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- 2K Mobile Toilet 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- 4K Mobile Toilet 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Microfiber Pinic Towel 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Gesture Phones S3 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
 Menu
Menu























 Favorites
Favorites



 Frequent updates ensuring high quality data
Frequent updates ensuring high quality data
 Over 5000 customers trust us to help grow their business!
Over 5000 customers trust us to help grow their business!

 Menu
Menu