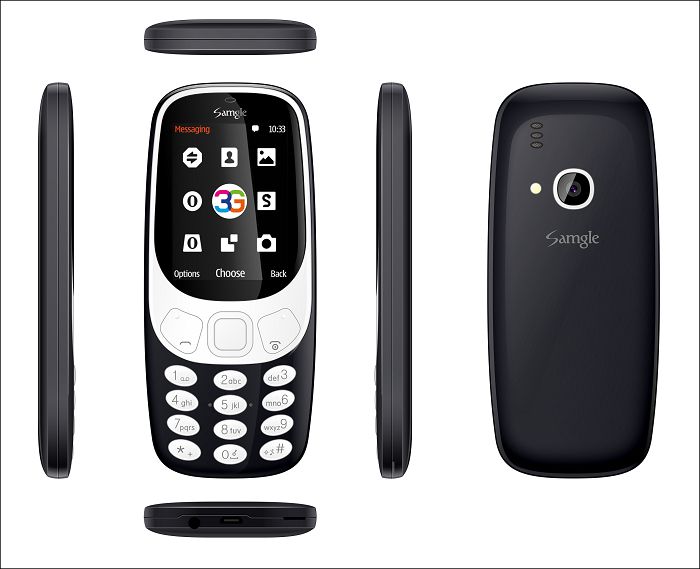



3310 Cheap 2.4-inch 3G Feature Phones
-
Min Order
1
-
Product Unit
Pieces
-
Origin
China Mainland
-
Payment


- Contact Now Start Order
- Favorites Share
- Description
Product Detail
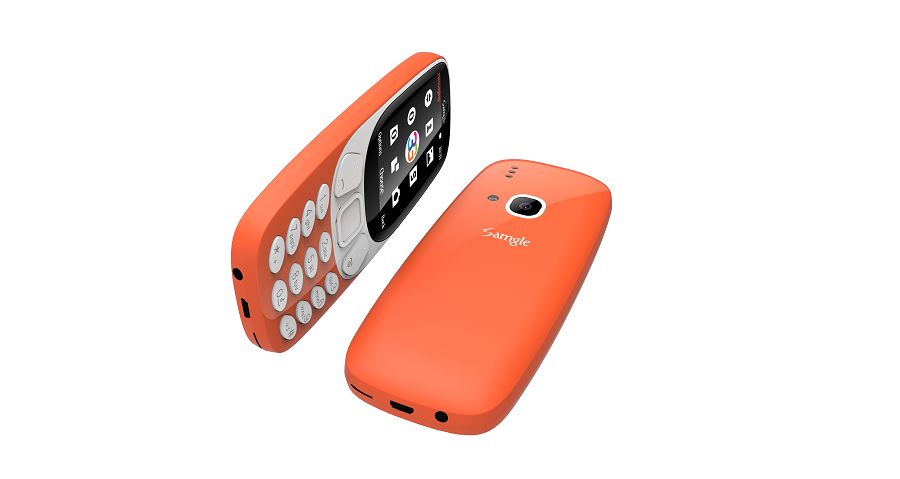
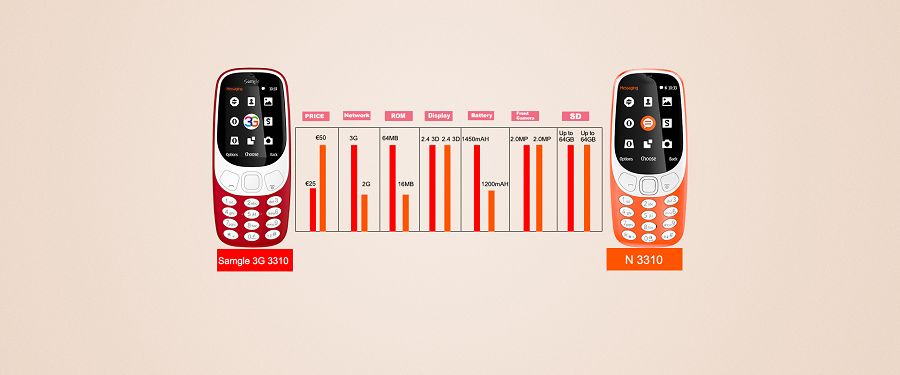
One of the biggest advantages of both the Samgle 3310 3G is their screen. It's 3D screen 2.4 display.
Display:2.4" inch curved window
Storage:128MB+64MB
Support micro SD (T-Flash):Max to 32GB
Camera:Rear SW 2.0M
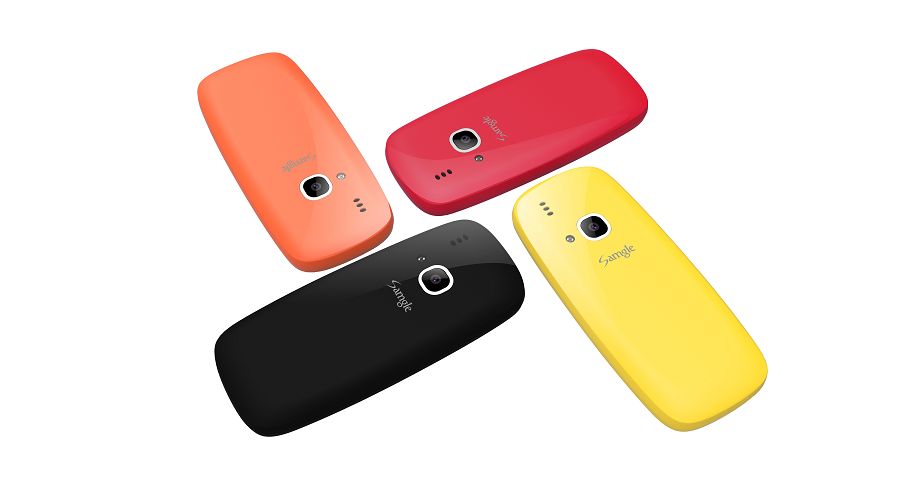
Color:Orange?Black?Yellow?Red?Blue
Wireless & Networks
Band Details(EU):
GSM:B2/B3/B5/B8 (1900/1800/850/900)
WCDMA:B1/B8 (2100/900)
SIM Card Type: SIM + SIM + TF
Language:English, Espanol, Portuguese, Italian, German, French, Russian, Arabic, Poland, Dutch, Bahasa Melayu, Chinese, Hindi, Tamil, Thai, myanmar,
SIM:Dual sim dual standby, Dual SIM; SIM1 is 3G, SIM2 is 2G
Dimension and Weight
Product size: 5*126*14.3mm
Product weight:64.5g
Battery weight:32g
Package size:142*136*35mm
Package
1 x Phone
1 x Battery (1450 mAh)
1 x AC power charger adapter ( 100~240V / EU plug)
1 x English user manual
NOTE
*The actual size and weight of the phone may vary due to different specifications and assembly tolerance
*The above data were gathered in tests in a lab environment. To avoid phone damage or malfunctioning
please avoid using your phone under extreme conditions















Q: Can I receive text messages with this phone?
A: Yes, the item can support the function.
Q: Is this Phone 3G or 2G capable?
A: 2G GSM: GSM 850/900/1800/1900MHz.
3G WCDMA: 900/2100
Q: This will work in India
A: Please ensure local area network is compatible. click http://maps.mobileworldlive.com/ for Network Frequency of your country. Please check with your carrier/provider before purchasing this item.
Networks:
2G: GSM 850/900/1800/1900MHz
3G WCDMA: 900/2100
Q: i bought this phone but i dont thibnk it works in australia Does it work in australia
A: It can be work in Australia.
Networks:
2G: GSM 850/900/1800/1900MHz
3G WCDMA: 900/2100
Languages: English, Espanol, Portuguese, Italian, German, French, Russian, Arabic,
Poland, Dutch, Bahasa Melayu, Chinese, Hindi, Tamil, Thai, myanmar,
Q: hello i d ask how may dais last the battery and if work with 3g sim cards
A: Normal standby time is around 300 hours. It will work with 3G network. SIM1 is 3G, SIM2 is 2G
Q: Hi, can this product ship to Argentina?
A: We can ship to your country by
Unregistered Air Mail 15 - 35 business days $1.10
Registered Air Mail 10 - 25 business days $3.01
Expedited Shipping 3 - 7 business days $43.81
Q: Will this phone support network service providers in Canada?
A: It just can work with Networks:
What is the Difference Between GSM and CDMA?
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) and Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) are two competing standards in cellular service. They both have derivatives for use with 3G phones known as Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) and CDMA2000, respectively. The major difference between the two technologies is how they turn voice data into radio waves and how the carrier connects to the phone. Other differences include the coverage area, the data transfer speeds, and the type of hardware used.
Coverage
Some areas and countries only have one technology available, so users should be sure to review coverage maps before buying a phone. Generally speaking, CDMA is most commonly found in North America and some parts of Asia, while GSM is found in most other places. Some carriers do offer international or "world" phones that can work with both, but if the phone is going to be used predominantly in one area, it may make sense just to get one that's tied to one type.
Data Transfer Speed
Both technologies can be used with 3G standard phones, but 3G GSM speeds can be faster than 3G CDMA speeds, which can make a big difference for those who use their phones for social networking, email and streaming video. The fastest 3G standard used with CDMA2000 is EV-DO Rev B., which has downstream data rates of about 15.67 Megabits per second (Mbit/s). The fastest standard available with UMTS is HSPA+, with downstream speeds of up to 28 Mbit/s.
Hardware
GSM phones and CDMA phones also use different types of smart cards known as Universal Integrated Circuit Cards (UICC). These are small removable cards that can be used to store information like a contact list and activate, interchange, and upgrade phones without carrier intervention as long as the phone is unlocked. This means that the carrier makes it possible for phone to work even if the end user removes and changes the card. Though both types can be sold locked, this is more common with CDMA phones.
UICCs can be programmed to work with either GSM or CDMA and their derivatives, or with both. Those that only work with GSM phones are called Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) cards and those that only work with CDMA phones are called CDMA2000 Subscriber Identity Module (CSIM) cards. There are also a few types of UICCs that are programmed to work with GSM, UMTS, CDMA, and CDMA2000, including CSIM/USIM cards and Removable User Identity Module (R-UIM) cards.
Roaming
Generally speaking, both networks have fairly concentrated coverage in major cities and along major highways. GSM carriers, however, have roaming contracts with other GSM carriers, allowing wider coverage of more rural areas, generally speaking, often without roaming charges to the customer. CDMA networks may not cover rural areas as well, and though they may contract with GSM cells for roaming in more rural areas, the charge to the customer can be significantly higher.
International Roaming
Some GSM and CDMA carriers offer international roaming, which means users can still use their phones when traveling abroad. To work internationally, the phone has to be a quad-band phone, which means that it works with frequencies of 850, 900, 1800, and 1900 MHz. Additionally, the phone does have to be unlocked and the user does have to be trying to use a network that exists in the country, which is sometimes more difficult to do with CDMA since fewer countries have CDMA networks. If the phone is unlocked and there is a network present, though, then users can buy a UICC with minutes and a local number in the country in which they're traveling to avoid paying international rates.
4G
Things get a little bit more complicated when it comes to phones with 4G. Most US cellular carriers use CDMA. 4G phones generally use LTE (Long Term Evolution), a high speed wireless broadband technology. In most of the world, GSM is preferred and 4G phones with LTE outside of the US use this service. In the US, however, US cellular carriers offering 4G phones have made the switch to LTE on the CDMA service. It is possible to determine which service a smartphone uses with the model number of the phone. Phone manufacturers or the cellular carrier can clarify this information. As of 2014, users in the US are most likely using CDMA. With the exception of countries like Russia and Japan, which continue to use CDMA like the US, most other countries in the world use GSM for 4G.
What Is a 3G Data Card?
A 3G data card is a card or chip designed to be inserted into a laptop or desktop computer to allow access to wireless Internet from a nearby tower broadcasting a 3G signal. Certain cell phones and smartphones have similar cards built in to enable access to cellular data as well as voice-based telephone connectivity. Though 3G networks are still prevalent in some places, they have been largely superseded by 4G and long term evolution (LTE) networks that offer faster, even more reliable connections and transfer rates. The 3G network first came into being in 1998, and at that time was the fastest Internet ever seen. Computers with data cards became popular around that time, and the cards were often advertised as a means of accessing the online realm quickly and reliably from almost anywhere. The cards had a number of limitations, though. The advent of newer, faster networks has rendered many of these cards obsolete today, as their functionality depends on ready access to 3G signals — which are being phased out in many places around the world.
Understanding 3G technology Generally
3G technology refers to the third generation in wireless digital network standards. Overall it is an upgrade to previous 2G networks, providing faster download speeds and greater reliability. It offers greater security and a wider range of application as well, such as streaming TV and video conferencing. 3G networking was the most advanced and fastest way to access the Internet until 4G networks were developed in 2008. Technology is still advancing, and every year seems to bring faster, better ways to get online.
Most 3G cards are designed only to work over 3G connections, which means that they may not work well if at all in areas where 3G signals are no longer broadcast. A lot of this depends on location. In very saturated areas, telecommunications companies have often elected to upgrade all of their towers and operating equipment to transition to the newest, fastest network. This often is a good way to provide more consistent results to a high volume of users at once. In more rural or remote areas, though, there isn’t always enough of a base to justify an upgrade, and as a result some regions do still support 3G technology. Data cards will usually still work in these places.
Transportability
When data cards for the 3G space were first introduced, transportability was often the benefit they were most associated with. With this card, location no longer limited users: they didn’t have to be in a wireless hotspot or in the vicinity of an established network in order to connect. The card also freed the user of bulky equipment, such as Ethernet cables, that must physically plug into modems.
3G data cards wirelessly access the 3G broadband networks established by carriers through interconnecting cellular towers. These towers transmit Internet data across electromagnetic wavelengths, known as spectrum, between devices. Users can download information, check e-mail, visit Web sites, and watch television on their laptops while riding in a car, sitting in an airport, or spending the day on a boat. These cards are often the most useful for people who don't have traditional cable or DSL Internet service at their homes, but who can receive cellular service from nearby towers.
Speed and Reliability
Most wireless carriers sold 3G data cards in their heyday, and carriers are still the source of data cards of more modern speeds today. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, 3G compatibility was usually the fastest and most reliable around, which usually served as a major selling point. The speed and reliability generally vary based on each carrier’s network. Most wireless carriers offer different varieties, often referring to them as 3G PC cards, air cards, and 3G mobile cards. These cards may interface differently with the computer. For example, some may require a PC card slot, while others may use a USB port.
In addition to the initial purchase fee, users also usually need to pay for the data they use, much as they would on a traditional cell phone plan. Most wireless carriers offer plans for their 3G cards that provide tiered levels of data downloading or, generally for a higher price, unlimited Internet access.
Limitations
3G data cards, while convenient, may have limitations as well. Wireless carriers typically offer varying download speeds for transmitting data. The cards often use a wirelessly broadcast data signal to transmit information, which is dependent on the quality of the towers in use. Cards connecting to older towers using slower spectrum bands may have a harder time transmitting large packets of data, and the same is often true for those connecting to newer towers: 3G data is often deprioritized today, which means that download times are often a lot slower.
The reliability with which a data card connects to the Internet may also be limited by the number of towers within its range. A wireless carrier with few established cellular towers provides a smaller coverage area and less reliable connections than a wireless carrier with a denser tower coverage map. If coverage remains too low, a card may not connect to the Internet at all.
How Do I Choose the Best Cell Phones for Kids?
When choosing cell phones for kids, be sure the mobile phone you choose is user friendly and age appropriate. You also need to consider the cell phone plan and how much it will cost. Even if cost is not an issue for you, a smart phone with multiple features may be unnecessary and too complicated for a young child to operate. If the child requires nothing more than basic call and text features, choose a basic-feature phone. Before you decide, however, visit the mobile phone carrier of your choice and speak with a representative for advice.
Basically, there are two options when choosing cell phones for kids. You can choose a no-contract phone, or one that will require a contract to operate. The contracts are generally one- or two-year plans. If you already have a cell phone plan, you might be able to receive a special rate for a family plan that includes two or more family members.
The advantage of a contract phone is a discount pricing. Also, you might find more of a selection for contract phones than on the pay-as-you-go, no-contract cell phone. Conversely, if your child simply needs an inexpensive cell phone without the obligation of contract or costly monthly plans, you should consider the no-contract phone. Some no-contract phones may require a plan, while others let you refill minutes with a phone card or credit card.
As you contemplate your options for cell phones for kids, consider the available data plans, which often limit usage and include fees if you go over your limit. Unless the child is extremely careful and responsible, he could inadvertently go over the limit on data usage, which could amount to exorbitant costs. If you choose a multi-media cell phone with limited data usage, you can ask your cell phone carrier to block all data on your child's phone, so there's no need to constantly monitor his usage.
There are a few other important things to consider before deciding which cell phone is right for your child. When choosing a cell phone for very young or pre-teen children, be sure it has a speed-dial function so your child can easily dial you without having to fumble through settings or pages. Another good idea is to choose a cell phone with a rugged exterior for durability. Also, cell phones for kids should be equipped with a protective case, so be sure there are phone cases available for the mobile phone you're considering.
- Mobile Bridge 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Crane 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Bridge 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Bridge C 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Bridge 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Lifts 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Magic Box Mobile Powerbank 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- 12000 Giant Mobile Power 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Cel Phones 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- HSP Mobile NET Device 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Speaker 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Cleaner 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Toolbox 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Cranes 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Billboard 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Mobile Lift 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- 2K Mobile Toilet 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- 4K Mobile Toilet 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Microfiber Pinic Towel 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Gesture Phones S3 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
 Menu
Menu
























 Favorites
Favorites



 Frequent updates ensuring high quality data
Frequent updates ensuring high quality data
 Over 5000 customers trust us to help grow their business!
Over 5000 customers trust us to help grow their business!

 Menu
Menu