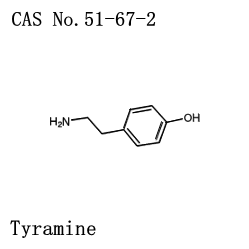
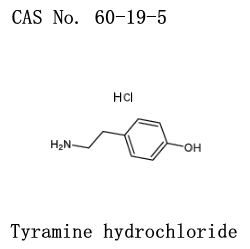
Tyramine CAS 51-67-2
-
Min Order
1
-
Product Unit
Pieces
-
Origin
China Mainland
-
Payment


- Contact Now Start Order
- Favorites Share
- Description
Product Detail
Tyramine Basic Information
Classification: Pharmaceutical Intermediate
Product name: Tyramine
Cas no.: 51-67-2
Product Alias: 4-(2-Aminoethyl)phenol, 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethylamine, 4-hydroxyphenethylamine, 4-(2-aminoethyl)-pheno; 4-(2-Aminoethyl)-phenol (thyramin); 4-hydroxy-benzeneethanamin; 4-Hydroxy-beta-phenylethylamine; alpha-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-beta-aminoethane; Benzeneethanamine, 4-hydroxy-; beta-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethylamine; beta-Hydroxyphenylethylamine
Molecular Formula:C8H11NO
Molecular Weight: 137.18
EINECS: 200-115-8
Standard: Enterprise standard
capacity production: No less than 40 tons per month
Description: off-white to white crystal powder
Loss on drying: 0.5% max
Assay (HPLC) : 99.0% to 101.0%
Single impurity: 0.5% max
Total impurity: 1.0% max
Usage: organic synthesis intermediates, as pharmaceutical intermediates; as adrenergic agonist and vasoconstrictor
Product Categories: Pharmaceuticals; Anilines, Aromatic Amines and Nitro Compounds; Amines; Aromatics; Intermediates and Fine Chemicals
Tyramine Chemical Properties
Tyramine Chemical Properties | |
bp | 160-162°C(lit ) |
| bp | 175-181°C8 mm Hg(it ) |
| FP | 165°C |
| FEMA | 4215 |
| Merck | 9835 |
Water Solubility | 1g/95mL (15 C) |
Stability | Stable.Incompati ble with strong acids,strong oxidizing agents. |
storage temperature | Refrigerator,Under lnert Atmosphere |
CAS DataBase Reference | 51-67-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
NIST Chemistry Reference | Phenol,4-(2-aminoethy)-(51-67-2) |
E PA Substance Registry Syste | Phenol,4-(2-aminoethy)-(51-67-2) |
Tyramine Description
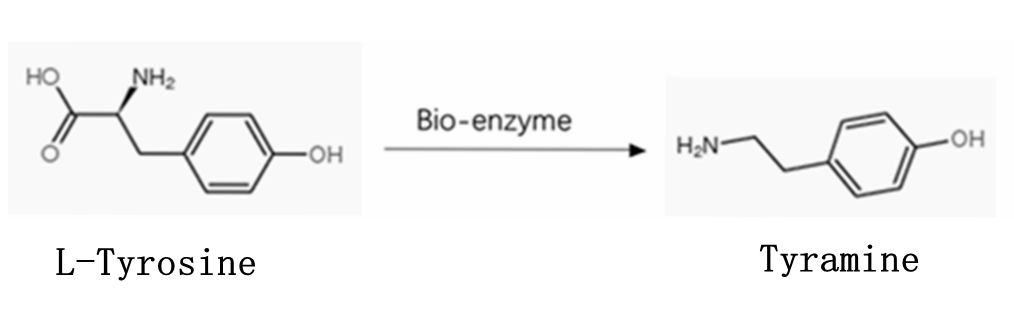
Tyramine, also called 4-(2-Aminoethyl)phenol, is a natural compound commonly found in plants and animals. 4-(2-Aminoethyl)phenol can also be manufactured from tyrosine an amino acid that exists in many foods.
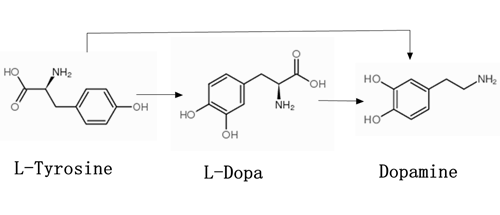
Tyramine is an amine and is derived from ammonia. In the human body, tyramine is called 4-casein, which is responsible for releasing catecholamine, which is secreted into the blood by the adrenal gland.
Some of the released substances include dopamine, norepinephrine and adrenaline. When these hormones enter the blood, the systolic pressure and the rate of heartbeat increase. This rise in blood pressure is often dangerous for people who take monamine oxidase inhibitors. Because monoamine oxidase is the natural mechanism of the human body to eliminate the excess tyamines. If a monoamine oxidase inhibitor is used, the level of tyramine increases and the risk of stroke increases. This is also the reason why people who eat tyrosine food are not advised to take a monoamine oxidase inhibitor.
The food containing this compound includes fermented food such as pickles, soy sauce and red wine, as well as old foods, such as cheese and pickled meat, etc. In addition, the avocado, chocolate, Vicia bean and pineapple also contain a large amount of tyamines.
Although there are no final findings, many people suspect that tyramine has a causal relationship with some people's migraine. It is speculated that it affects the vascular system by releasing catecholamines and indirectly leading to the contraction of the head. Then the blood vessels are inflated after the effect of regression, and thus leads to migraine. Sometimes, migraine patients avoid tyramine - containing food to be significantly relieved.
The relation with Tyrosine
Tyrosine can be converted to many bioactive substances, such as dopamine, tyramine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, thyroxine, melanin, protopine and papaverine, ect.
Tyramine quality
- Flange Connection 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Self Fusing Insulating Clay 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Gravity Casting 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Pulling And Inserting 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- FF582 rapier loom tucking 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Carving Cornice Mouldings 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Tri Racing Belt for Running 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Trolley Valise Hot Selling 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Loading Dock Lift Between Two Building 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Tyramine HCl CAS 60-19-9 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Heating Core For Culture Insulation Lamp 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Top Treadmills For Running 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
 Menu
Menu










 Favorites
Favorites


 Frequent updates ensuring high quality data
Frequent updates ensuring high quality data
 Over 5000 customers trust us to help grow their business!
Over 5000 customers trust us to help grow their business!

 Menu
Menu